Table of Contents
-
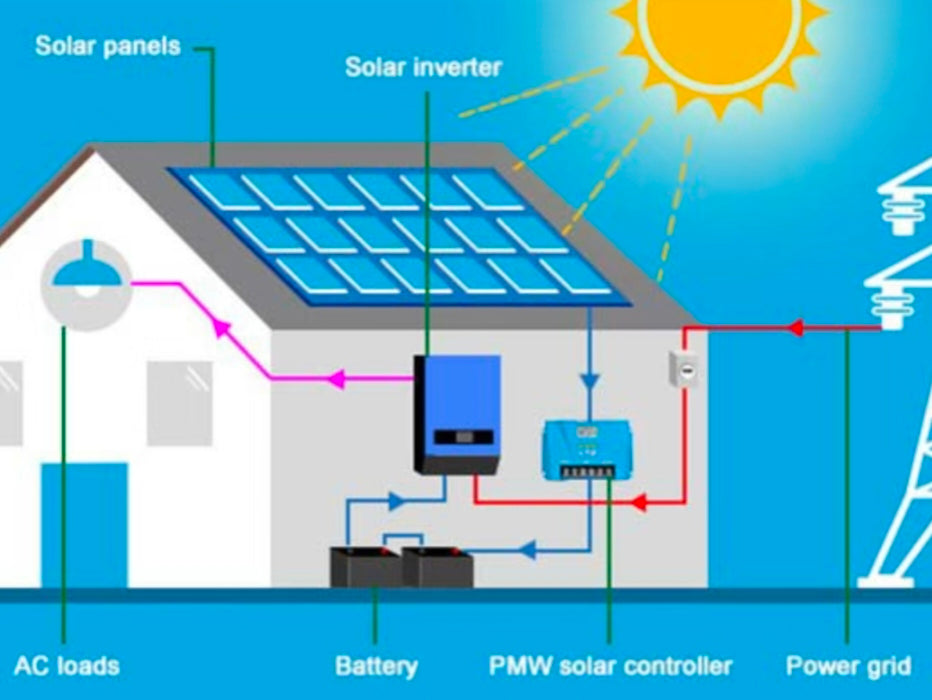
What Is a Solar Inverter?
-
What Is a Single-Phase Inverter?
-
What Is a Split-Phase Inverter?
-
What are the differences between single-phase inverters and split-phase inverters?
-
How to choose what suits you?
-
Final
What Is a Solar Inverter?
In the ocean of knowledge,Solar panels generate direct current (DC) —think of this as the type of power a battery provides. But nearly all home appliances ( TVs, refrigerators, air conditioners) run on alternating current (AC) , which is what comes out of wall outlets.
Solar inverters are the assistants that help convert between these two types of power sources.It can convert the direct current generated by solar panels into alternating current that can be used in homes.
What Is a Single-Phase Inverter?
A single-phase inverter is the most basic and widely used type of inverter for residential solar systems.
As the name suggests, it produces a single AC voltage signal that powers your home’s appliances. You can think of its output as a single, steady wave of electricity—simple, reliable, and perfect for most small to medium-sized homes.
What Is a Split-Phase Inverter?
A split-phase inverter is a specialized type of inverter.
single-phase inverters that produce one AC signal, split-phase models generate two separate 120V AC signals that are 180 degrees “out of phase”
When these two 120V signals are combined, they create a 240V AC output. This dual-voltage design is key: it lets the inverter power both small 120V devices and large 240V appliances, without the need for extra transformers or adapters. It’s like having two power “channels” in one device.
What are the differences between single-phase inverters and split-phase inverters?How to choose what suits you?
let’s break down their core differences in terms of voltage output, compatibility, and use cases.
1. Voltage Output
Single-phase: Produces one AC voltage
Split-phase: Produces two 120V AC signals and a combined 240V signal. Supports both 120V and 240V devices simultaneously.
2.Compatibility
Single-phase: Suitable for low-power single-voltage loads for example household appliances
Split-phase:Compatible with both 120V low-power loads and 240V high-power loads
3.Wiring Complexity
Single-phase:Simple wiring: only need to connect the inverter output to the single-phase grid or off-grid load.
Split-phase:Relatively complex: requires distinguishing two live wires (L1, L2) to avoid phase mismatch, which may need professional installation.
4.Cost
Single-phase: Lower Cost,Simpler circuitry means single-phase inverters are typically 10–20% cheaper than split-phase models.This makes them a budget-friendly option for small homes.
Split-phase:Higher cost due to more complex internal circuits and higher power capacity.
5.Ideal Use Cases
- Single-phase: Small to medium homes with standard appliances (no large 240V devices), small solar setups (e.g., balcony solar, tiny homes), or regions with single-phase grids.
Split-phase: North American homes with mixed 120V/240V appliances, large solar systems, or hybrid/off-grid setups that need to power heavy-duty equipment.
How to Choose the Inverter That Suits You?
The selection depends on your load type, power demand, regional grid standards, and budget.Sunboost offers both single-phase and split-phase inverters, allowing you to choose according to your needs.
1. Check your regional grid voltage standard
If you live in Europe, Asia, Australia, where the residential grid is 230V single-phase, a single-phase inverter is the default choice (unless you have 400V three-phase heavy loads).
If you live in North America (US, Canada), where the residential grid uses 120V/240V split-phase, choose a split-phase inverter if you have 240V appliances (e.g., electric dryer, central air conditioner).
We ship a large number of 6.2kW phase-split inverters to the United States every month, which is essential for the North American market.

2. Evaluate your total load power and load type
- Choose single-phase inverter if:
Your total load power is less than 10kW.
You only use low-power 120V/230V appliances (no 240V high-power equipment).
Example: Small home, apartment, or off-grid cabin with basic lighting and small appliances.
-
Choose split-phase inverter if:
Your total load power exceeds 10kW, or you have 240V high-power devices (air conditioner, electric water heater, EV charger).
You plan to expand your solar system in the future (split-phase inverters have better scalability for heavy loads).
Example: Large family homes, small workshops, or farms with multiple heavy electrical devices.
3.Consider budget and installation complexity
- If you have a limited budget and simple load needs, a single-phase inverter is more cost-effective and easier to install.
- If you need to power 240V equipment, the higher cost of a split-phase inverter is necessary (it avoids the need for two separate single-phase inverters).
Final
Solar inverters are the unsung heroes of your solar system, and choosing the right type—single-phase or split-phase—ensures your system runs efficiently and powers all your appliances.
If you’re looking for an efficient, stable power conversion solution for a variety of applications, consider a split phase inverter.
Of course, split-phase inverters are specifically designed for mixed-voltage systems in North America, while single-phase inverters are suitable for most homes. I hope my introduction has been helpful.